The aperture phosphor coated lamps that jelight company produces employ the same basic design as the double bore low pressure mercury vapor lamps with the exception of a special phosphor coating.
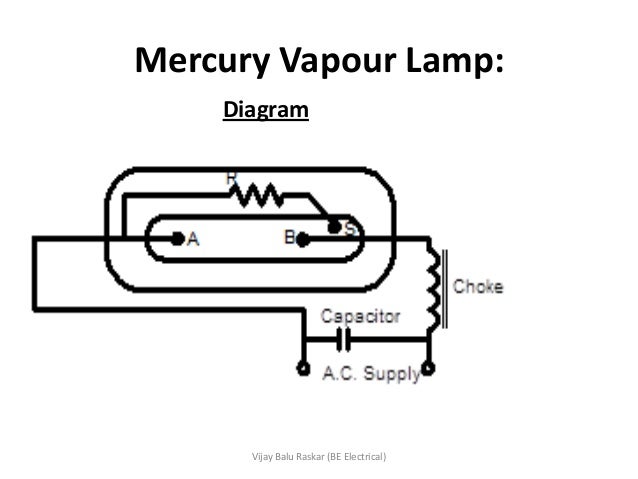
Low pressure mercury vapour lamp circuit diagram.
As the main arc strikes and the gas heats up and increases in pressure the light shifts into the visible range and the high gas pressure causes.
When a mercury vapor lamp is first turned on it will produce a dark blue glow because only a small amount of the mercury is ionized and the gas pressure in the arc tube is very low so much of the light is produced in the ultraviolet mercury bands.
A sodium vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light at a characteristic wavelength near 589 nm.
This coating covers more than 70 of the diameter of the lighted length of the lamp.
A fluorescent lamp is a low weight mercury vapour lamp that uses fluorescence to deliver visible light.
Again transition of the electrons requires least amount of input energy from a colliding electron.
Rather than a cold spot the lamp s amalgam spot on pellet regulates mercury vapor pressure during operation and yields up to three times the uvc output of a standard low pressure mercury lamp of the same length.
An electric current in the gas energizes mercury vapor which delivers ultraviolet radiation through discharge process and the ultraviolet radiation causes the phosphor coating of the lamp inner wall to radiate visible light.
Amalgam lamps use a mercury amalgam mix to control mercury vapor pressure.
In case of fluorescent lamp the mercury vapour pressure is maintained at lower level such that 60 of the total input energy gets converted into 253 7 nm single line.